certainly looks tame compared to last year’s
*Takes off helmet*
*Shows kindly & benign face*
On a day when Singapore’s working class was left to reflect on their social standing in the current status quo, May 1st (by virtue of its proximity to the Mids) has traditionally been Miss Loi’s Day of Labour.
But with the advent of The Temple, the distance travelled is much less this year, with a corresponding drop in the number of stunts overtaking manoevuers needed in order to get to her students’ place on time.
Which also means that Miss Loi actually has time to help that butchy Sergeant Loi (who is on leave today and thereby sparing the serene Temple Grounds from her KPKB for the first time this week) post her Matrices notes:
Ever since the bulk of the Matrices chapter has been migrated over to the New EMaths Syllabus, according to Section 1.4 of the AMaths Syllabus, about the only time you’ll ever see matrices appearing in your AMaths papers would be when you’re asked to solve a pair of simultaneous equations using the inverse matrix method.
The following, then, is really all you need to know 🙂
Solving Simultaneous Equations Via Inverse Matrix
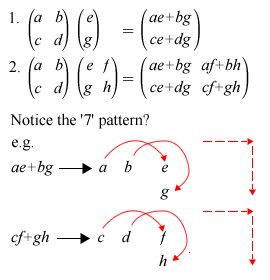
A. HOW TO MULTIPLY MATRICES
B. DETERMINANT OF A 2X2 MATRIX
Determinant of matrix M = 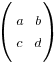 is given by:
is given by:
|M| = 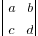 = ad – bc
= ad – bc
If |M| = 0 ⇒ M is singular.
If |M| ≠ 0 ⇒ M is non-singular.
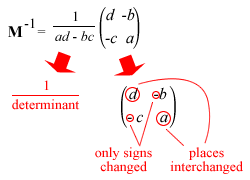
C. INVERSE OF A 2X2 MATRIX
For a non-singular matrix M =  ,
,
D. THE INVERSE MATRIX METHOD
AX = B ⇒ X = A-1B
*Note: AX = B does NOT ⇒ X = BA-1!
SAMPLE PRACTICE QUESTION
Use the inverse matrix method to solve the simultaneous equations:
5x + y = -8
–x + 2y = 17
Ans:
*See the words inverse matrix method in question – SIANZ!*
Can you see that the pair of simultaneous equations are actually part of matrix multiplications shown in A above? So you can convert to matrix form:

You can then move the 2 x 2 matrix to the
RHS of the equation as highlighted in D above:

Now to find the inverse matrix
 :
:As described in B above:
Determinant → = (5)(2)-(1)(-1) = 11 ≠ 0
= (5)(2)-(1)(-1) = 11 ≠ 0
⇒ non-singular
⇒ inverse exists!As described in C above:
So
Sub the inverse into the equation in step i:

Do your multiplication! As described in A above:


⇒ x = -3, y = -7Note: most of the time, you should end up with a 2 x 1 matrix after multiplying.
Know with true faith the methods above. Be cautious with the pointers and common mistakes in red. Understand with thy heart the representative sample question at hand.
Print this out if necessary and commit to memory the above procedures, and be comforted that no matter what happens, Miss Loi shall always be here to support you, in spirit and in soul.
HAPPY LABOUR DAY!
*Drifts away like 倩女幽魂*
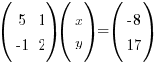
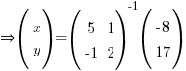
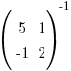 :
: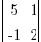 = (5)(2)-(1)(-1) = 11 ≠ 0
= (5)(2)-(1)(-1) = 11 ≠ 0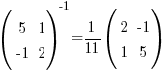
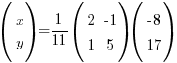
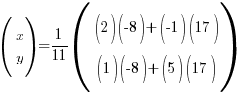
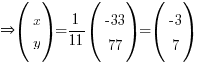
 Miss Loi is a full-time private tutor in Singapore specializing in O-Level Maths tuition. Her life’s calling is to eradicate the terrifying LMBFH Syndrome off the face of this planet. For over years she has been a savior to countless students …
Miss Loi is a full-time private tutor in Singapore specializing in O-Level Maths tuition. Her life’s calling is to eradicate the terrifying LMBFH Syndrome off the face of this planet. For over years she has been a savior to countless students …